“Global shift to renewable energy brings increased attention to environmental protection and consequences of policy violations”
The global shift towards renewable energy has led to increased investments in clean technologies, but the environmental risks associated with these projects cannot be ignored. Fines and penalties for environmental violations have also increased, making it crucial for companies to prioritize environmental protection as part of their operation philosophy. From planning to operation, companies involved in green technology assets must take special care to ensure compliance with environmental policies to prevent reputational and financial losses.
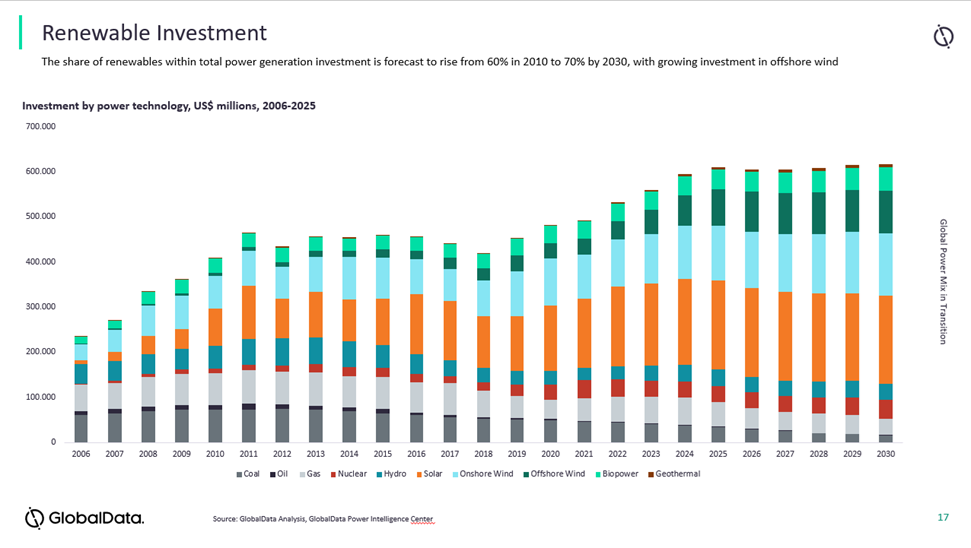
Governments, utilities, companies and multilateral financial organizations around the world have focused their attention on renewable energy. This view has changed the global energy outlook in recent years and in the decades to come. Especially in the generation segment, major efforts and investments have been made to switch from fossil fuel energy to renewable energy.
In its Energy Technology Perspectives, the International Energy Agency IEA have stated on the subject: “The global clean energy transition is accelerating, driven by a combination of policy, technological change and economics. The need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions drastically and urgently in the face of ever more startling evidence of global climate change is now widely accepted, reflected in increasingly ambitious national goals.” 13 In its Global Power Mix Transition 2021 – 2035 by GlobalData added, “By 2035, almost 50% of the global demand will be powered by renewables, supported by increasing investments in clean technologies.” 2
Countries such as Australia have set themselves a date to achieve their pathway to Zero Net Emissions by 2050, despite being one of the world’s leading per capita emitters of greenhouse gases. They have analyzed and, to achieve this goal, the government must invest at least 20 billion and are relying on the private sector to invest even more.3
Experts agree that by 2035 almost 50% of the world demand for energy will be supplied by renewables. But as investments soar and green assets are deployed everywhere, the standards and expectations on environmental protection of stakeholders and authorities have risen too. Today, fines and penalties are higher than ever. A single incident can have enormous reputational and financial consequences.
Countries such as the United Kingdom have taken violations of environmental policies very seriously and have raised fines and civil penalties, which today can amount to up to £250 million. After fining 33 companies £27 million, Liz Parkes, Deputy Director of Climate Change at the Environment Agency, said: “The fines published today should serve as an important reminder for all organizations to ensure that they are compliant with these schemes and are playing their part in tackling climate change.4”.
This scenario forces all companies involved in the financing, development, acquisition, start-up and operation of green technology assets. To take special care with environmental protection, not only as a legal duty, but to extend it to the operating and organizational philosophy, as it can be decisive to obtain permits and get the work done, to smooth relations with local authorities and surrounding communities, to ensure financial success and, to preserve and build a better reputation of the company.
Let’s have a look at what happened in 2020 at the GPPC Pipavav power company, which operates Asia’s largest solar farm. On the night of July 10, a fire broke out that lasted seven hours and affected the operation of the power plant and the power grid. At the time, Hitesh Patel, Deputy Engineer (Electrical) of GPCL stated, “The main control room of the company is completely charred, while transformers and other equipment have been damaged in the switchyard section…5.”. This single incident involved for a green power producer: loss of assets, financial losses and on-site investigations by the authorities.
All these environmental concerns impact projects from inception to operation. The authorities want people to have access to clean energy, but they closely monitor that the clean energy plant or power plant has been built with respect for the environment and for nearby water sources. This was the case in the United States, where the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Department of Justice announced on December 20 fines of more than $1 million for four solar farms under construction in Illinois, Alabama and Idaho. Larry Starfield of the EPA said “These settlements send an important message to the site owners of solar farm projects that these facilities must be planned and built-in compliance with all environmental laws.6. Furthermore, academics have gone ever deeper and are now talking about, not only about renewable energy; but where the assets come from, how and where they are made and what its carbon footprint is. On this subject Annick Anctil from Michigan University “We need to plan and choose panels considering not just the electricity production but the full lifecycle.”.
On the other hand, some projects have paid special attention to environmental protection from the outset. The Gharo Solar Photovoltaic Park in Pakistan is one of the projects that overcame the invisible danger of environmental pollution from the start-up phase thanks to a project that aimed to be clean from its conception.
In this 98-hectare solar park that produces 50.123 MW, they try to commit to producing clean energy and took additional measures to be concerned about environmental protection, especially to avoid fires, damage and spills and soil pollution with the installation of the Transformer Protector (TP) in their facilities. With this strategy, they not only avoid environmental disasters, but also secure key assets in a $43.7 million CAPEX project. In addition, the plant also contributes to saving 71,000 tons of CO2 emissions annually.
We can conclude that environmental protection is crucial, and the installation of TP is an effective way to prevent explosions and dangerous leaks that can damage the environment and threaten public safety. It also helps to reduce energy waste and improve the efficiency of the power grid. Coupled with the global shift to renewable energy, environmental protection has become a critical issue, and violations of environmental policies can have serious consequences. Therefore, with TP companies, utilities and countries can help prevent environmental catastrophes and secure assets in green energy projects, which is essential for both legal compliance and the success and reputation of these projects.
[1] Energy Technology Perspectives 2023, International Energy Agency.
[2] GlobalData, Global Power Mix Transition 2021 -2035 Outlook report.
[3] Australia adopts target of net zero emissions by 2050 but won’t legislate goal
[4] More than 30 companies fined as part of efforts to reduce emissions
[5] GlobalData, Global Power Mix Transition 2021 -2035 Outlook report.
[6] The construction of four solar farms in the US violated the Clean Water Act